Joint Pain
TREATMENT
JOINT PAIN
Joint pain can occur due to various reasons affecting the health of our joints, like injury, inflammation, or arthritis. These connections between bones allow smooth movement, but disruptions in bones, cartilage, or synovial fluid can cause discomfort. Overuse, strain, or autoimmune disorders can also contribute.
At Revive, we provide tailored treatments to relieve pain, enhance mobility, and manage joint health. Our goal is to help you live fully with improved joint function and less pain.
TREATMENT OPTIONS
PRP
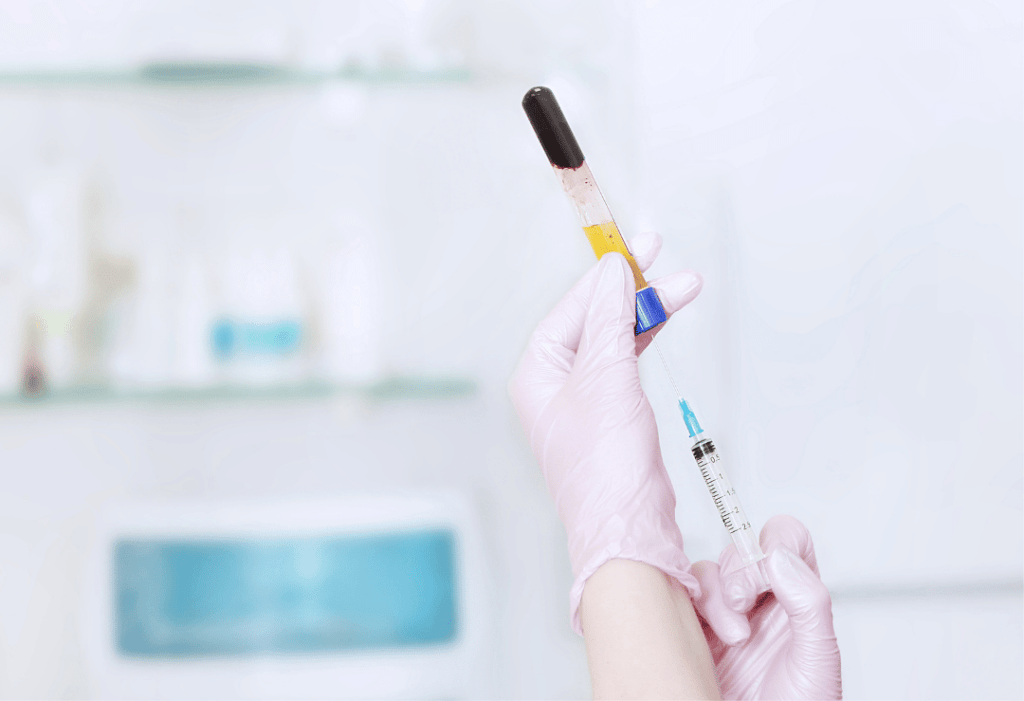
Concentrated platelets from your blood are used in PRP therapy and injected into the joint to encourage tissue repair and decrease inflammation. This minimally invasive procedure assists in relieving arthritis, tendonitis, and sports injuries, bringing about improved joint function and mobility for many without the need for surgery.
LASER
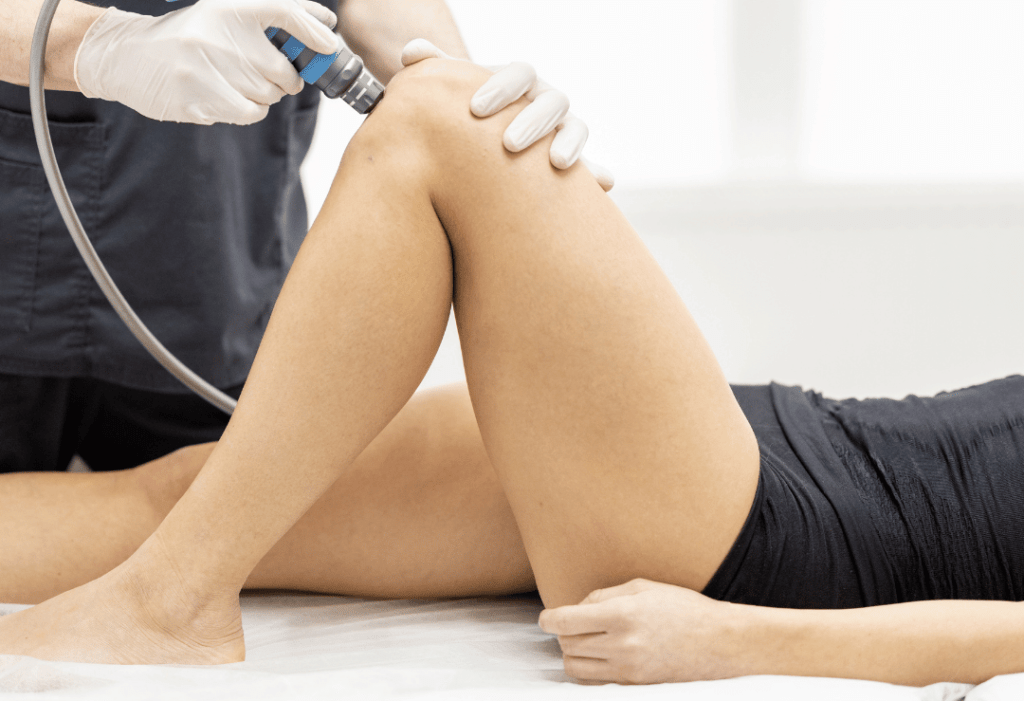
Fotona’s ComfortLase™ offers non-invasive joint pain alleviation through inflammation reduction and natural healing. This therapy efficiently cures arthritis and sports injuries, increasing mobility and comfort without requiring surgery or downtime. It also promotes wound healing, tissue regeneration, and pain relief, resulting in speedier recovery and better overall well-being.
IDEAL CANDIDATE
Based on the cause and severity of pain, the optimal candidate to manage joint pain differs. However, there are certain general characteristics that make someone relevant to joint pain treatment:
- Chronic joint pain sufferers
- Limited mobility due to pain
- Arthritis diagnosed individuals
- Joint injury victims
- Age-related joint degeneration
- Autoimmune disorder patients
- Seeking pain relief
TARGET AREAS
PRP therapy and Fotona laser ComfortLase can be used to treat joint pain by targeting different areas like:
- Knees
- Shoulders
- Hips
- Elbows
- Ankles
- Wrists
- Spine
- Neck
AVERAGE COST
OUR PORTFOLIO
Joint discomfort from illnesses such as arthritis and traumas can cause stiffness and swelling, interfering with normal activities. At our facility, we provide modern treatments such as Plasma Rich Platelet (PRP) therapy and Fotona laser treatments. PRP therapy naturally decreases inflammation and stimulates joint tissue healing, whereas Fotona laser treatments use non-invasive technology to relieve pain and enhance joint function via photobiomodulation. These treatments are intended to improve mobility and quality of life for our patients. Book Now →
LET’S CHAT
TELL US YOUR GOALS
FAQs
STAY IN TOUCH
Subscribe to stay informed about special promo deals, exclusive events, and insiders knowledge about all things aesthetics & wellness.
